Creating PCBs by hand is challenging and prone to mistakes. These PCB Design Software can help you design, test, and manufacture boards faster, easier, and with fewer errors.
If you are a beginner in printed circuit board (PCB) designing and are still manually creating schematics and layouts, which are prone to error, then stop. Or if you are a PCB designer, you might have faced issues like managing complex circuits with many components, validating circuit behaviour before manufacturing, handling component libraries and footprints accurately, etc. But not anymore. We have sorted a few PCB design tools for you.
Popular PCB Design Softwares
Now, what are these tools? Before understanding this, let us understand what electronic design automation (EDA) tools are.
EDA is a software applications that help engineers design, simulate, and prepare electronic circuits and PCBs for manufacturing. There are numerous EDA tools available on the market that are specifically designed for PCB design. They do the entire process, from creating circuit diagrams to the final layout and manufacturing.
Key components of such EDA tools include schematic capture for drawing circuits, PCB layout for placing components and routing connections, simulation and analysis tools to test designs, and verification tools to ensure they meet specifications.
Let us discuss a few examples to make it easy for you to decide which EDA tool to use for PCB design and when.
ExpressPCB: Free Windows-based PCB designing tool
ExpressPCB is a free Windows-only CAD software for creating PCBs. It features separate tools for drawing schematics, laying out boards, placing components, and routing connections. The schematics automatically update the PCB layout, supporting boards with up to six layers and designs up to 31 inches × 31 inches.
This tool is ideal for quick projects, education, and prototyping boards, with access to over 10,000 components. It has drag-and-drop functionality, multi-page schematics, design rule checking, and output of Gerber files, drill files, BOMs, and PDFs/PNGs.
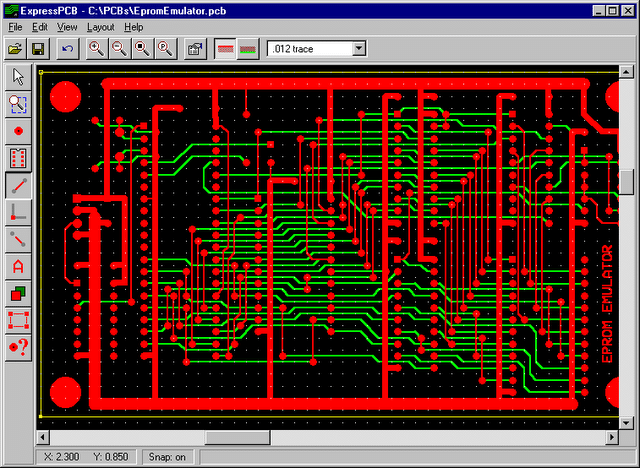
The latest version, ExpressPCB Plus 3.2 (June 2023), adds font rendering, parts preview via SnapEDA (an online library of components for schematics and PCB layouts), includes safety markings, and has updates for IoT and date codes.
The company says it is free to download. You can use it for designing boards, with no subscriptions or fees, and you only pay if you order physical PCBs. The software is proprietary, but it can be used for an unlimited number of projects. Know more about ExpressPCB.
DesignSpark: From Circuit to PCB
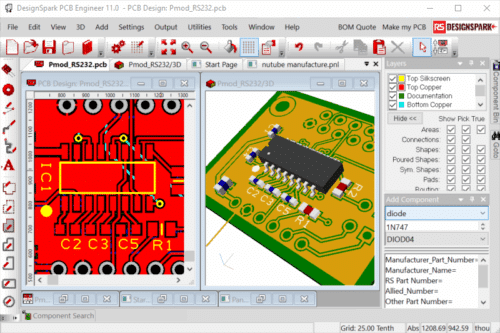
DesignSpark PCB makes designing circuit boards accessible by providing a free tool that takes us from a circuit diagram to the files needed for a manufactured board. It works for professionals, educators, students, and hobbyists, removing cost barriers.
The latest version, DesignSpark PCB 13 (released September 16, 2025), adds graphics and the option to set a component’s origin at the centre of its pads for precise layouts. Its interface, toolbars, shortcuts, and interaction bar make the workflow smooth, while the ModelSource library provides components and reference designs. Users can manage projects with multiple schematic sheets, and all components are linked to RS Components for purchase.
Unlike many design tools, DesignSpark PCB is free, with no trial periods, time limits, or feature restrictions. It supports boards up to 1 square metre, unlimited schematic sheets, and as many layers as needed. Learn more about DesignSpark.
LibrePCB: An open EDA for Engineers
Whether you are new to PCB design or experienced, LibrePCB is a free, open-source tool for capturing schematics, laying out boards, checking rules, exporting files, and sending boards for manufacturing.
It combines schematic capture, PCB layout, part management, and real-time rule checks in a single platform. You can export Gerber, Excellon, BOM, pick-and-place data, and HTML BOMs.
It works on Windows, macOS, and Linux with readable project files.
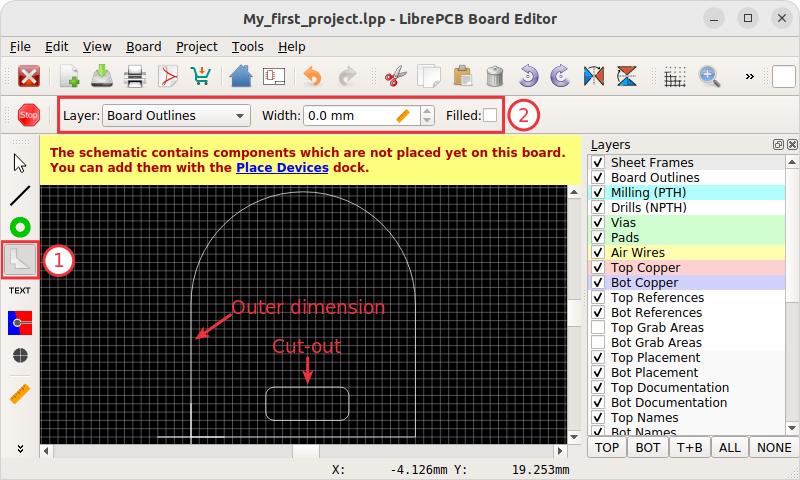
The latest version, 1.3.0 (March 2025), introduces HTML BOM export, enhanced KiCad v9 library support, refactors some modules in Rust for improved stability, and resolves crashes. Users like its library system and ease of use, though it is limited for complex boards.
LibrePCB is entirely free with no trials or subscriptions. Designed for students, hobbyists, and small teams, the latest version handles everyday designs. Check more details about LibrePCB.
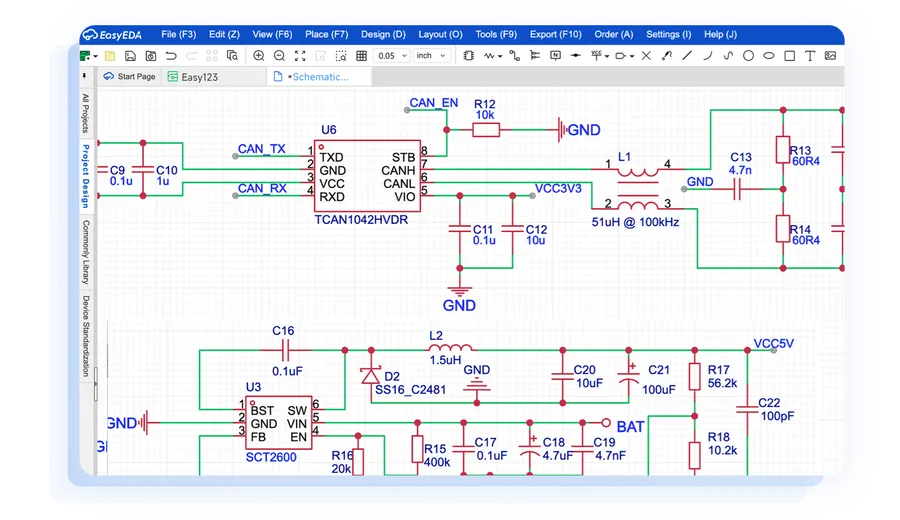
EasyEDA: A Cloud-based PCB Design Tool
Most professional CAD software needs strong hardware, but this tool runs in the cloud, making it usable on older systems and suitable for remote work. The latest update was made on April 8, 2025. It runs in the browser or as a desktop app on Windows, Linux, and Mac.
The Online Editor needs no installation and lets you store and share work in the cloud, work together in real time, track changes, and access data from anywhere.
EasyEDA is available in Standard, Professional, and offline versions, offering a single platform that combines schematic capture, PCB layout, and simulation. This allows you to seamlessly transition from concept to prototype without needing to switch tools.
EasyEDA is free for commercial use, with paid options offering private storage or faster support without altering the core editor. Users can run both Standard and Professional versions simultaneously. For more information, check EasyEDA details.
CircuitMaker: A Free PCB Tool We Can All Use
When we are trying to turn an idea into a real circuit, CircuitMaker comes in. It offers a free platform for schematic capture and PCB layout, supporting 16 signal layers, 16 plane layers, and no PCB size limits.
The latest release, CircuitMaker 2.3.0 (July 1, 2024), updates its component search system to utilise the Nexar API. This cloud service provides real-time data on electronic parts, including availability, pricing, and specifications. This update also allows users to import designs from KiCAD and P-CAD, making it easier to reuse work done in other tools.
The limits include file compatibility primarily with Altium formats and cloud-only storage, which means no local copies are available. Even with these limits, it remains useful for anyone who wants PCB design without a license and with access to community-driven features. Get more details about CircuitMaker.

EAGLE: Design the whole product, not just the PCB
EAGLE, now part of Autodesk Fusion, gives designers one platform for PCB work, simulation, mechanical modelling, manufacturing, and collaboration.
Access to EAGLE comes through a Fusion subscription, which merges electronic computer-aided design (ECAD) and mechanical computer-aided design (MCAD) so teams can work on the same project without switching tools.
Key features include SPICE simulation, modular design blocks, drag-and-drop placement with linked schematic and PCB views, automatic syncing, ERC and DRC, routing tools, online part libraries, and 3D PCB modelling.
A free EAGLE version is available for hobby and learning use, offering schematic capture, PCB layout, autorouting, and fabrication outputs, but with limits such as a 100 × 80 mm board size, two signal layers, and a small library.
The free license works on Windows, Mac, and Linux, includes full editors, supports basic PCB creation for personal projects, and allows fabrication outputs, though commercial work needs a paid license. Know more about EAGLE.
KiCad: A Free PCB Design Tool
KiCad is a free and open-source electronic design automation (EDA) suite that runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux, providing tools for schematic capture, PCB layout, 3D visualisation, and circuit simulation without usage limits, making it suitable for startups, small businesses, hobbyists, and educators.
The latest version of KiCad 9.0(released on July 7, 2025) adds features such as output jobsets for automated exports, routing tools, padstacks, multichannel layout support, component classes, visual DRC checks, ODB++ export, git integration, and a plugin API, supporting both basic and advanced workflows.
Its workflow separates schematic design and layout, enables reuse across multiple boards, and integrates with SPICE for circuit simulation.
Platform independence and zero cost make it accessible for open-source hardware projects, education, and prototyping, and users note its adoption even in professional designs. For more information, Check KiCad’s more details.
Pulsonix: A Professional PCB Tool
Pulsonix offers an EDA suite that encompasses schematic capture, PCB layout, and simulation. It is a paid commercial software, with a trial version limited to 100 component pins, allowing engineers to test its features before committing to a license.
Last version 14.0, released in October 2025, includes a fully integrated ngspice-based simulator (PulsonixSim) for transient, AC, DC, Monte Carlo, noise, and transfer function analyses directly within the schematic environment, 3D visualisation with Flexi Bend and clipping plane features, interactive HTML BOMs, scripting and automation, vault integration for version control, and support for high-speed, flexi-rigid, and embedded component designs.
You can perform revision analysis through graphical comparison tools, automate tasks with the scripting framework, and manage data with vault integration.
The trial version is helpful for small projects, education, or evaluation, while full features support electronics design, simulation, and management, helping engineers focus on innovation rather than tool limitations. Check more information about Pulsonix.

Altium Designer: One platform for PCB design
Whether you are new to PCB design or experienced, there comes a point when having schematics, simulation, PCB layout, and manufacturing tools in one place is useful. Altium Designer provides this.
The latest version, 25.8.1 (released July 16, 2025), provides a comprehensive EDA platform for PCB and product development, consolidating everything in a single environment from concept to final files.
You can draw schematics, route rigid, flex, or rigid-flex boards with live 3D views, run SPICE simulations and many more things.

Altium Designer is not free beyond a 30-day trial, which limits file saving, cloud access, updates, support, exports, and collaboration.
Students and schools can access free or discounted academic licenses.
There are some free extras, but they do not replace the full software.
Academic access lets students explore at no cost, but independent or professional designers need a paid license to use the full platform. Know more about Altium Designer.
PCB design platforms span a broad spectrum, each serving a different level of expertise and project requirements.
Free options are well-suited for newcomers or hobby projects, while cloud-based environments facilitate teamwork and remote access.
Some tools excel at quick prototyping, and others provide the depth needed for complex, production-ready designs.
Selecting the right one can significantly improve workflow efficiency, minimise mistakes, and ensure a smooth path from initial idea to a fully realised PCB.